Tibia fractures require a structured physiotherapy approach to restore mobility, strength, and function. These exercises are designed to promote healing, improve range of motion, and enhance overall recovery. A comprehensive guide, often available as a tibia fracture physiotherapy exercises PDF, provides detailed routines and expert advice for a successful rehabilitation journey.
Overview of Tibia Fractures and Their Impact on Mobility
Tibia fractures significantly impair mobility due to the bone’s critical role in weight-bearing and movement. These injuries often result in pain, swelling, and limited walking ability, requiring surgical intervention in severe cases. The fracture’s location, such as the tibial plateau or shaft, influences the severity and recovery process. Early physiotherapy is essential to restore function and prevent long-term mobility restrictions.
The Role of Physiotherapy in Tibia Fracture Recovery
Physiotherapy plays a pivotal role in tibia fracture recovery by enhancing mobility, strength, and functional independence. It addresses pain, swelling, and limited range of motion, promoting optimal healing. Customized exercises, such as non-weight-bearing movements and progressive resistance, help restore muscle function and joint stability. Regular physiotherapy sessions ensure a structured approach to recovery, minimizing complications and accelerating the return to daily activities and sports.
Importance of Early Rehabilitation
Early rehabilitation is crucial for optimizing recovery after a tibia fracture. It prevents stiffness, promotes healing, and restores function. Delaying therapy can lead to prolonged immobility, muscle atrophy, and reduced mobility. Early intervention enhances joint mobility, strengthens surrounding muscles, and minimizes complications, ensuring faster return to daily activities and improving long-term outcomes significantly.

Classification of Tibia Fractures
Tibia fractures are classified into types based on location and complexity, including shaft, plateau, and complex or simple fractures, each requiring tailored treatment approaches.
Tibia Shaft Fractures
Tibia shaft fractures occur along the main diagonal weight-bearing bone in the leg. These fractures can be closed or open, with varying degrees of displacement. Treatment often involves surgical intervention, such as intramedullary nailing, to stabilize the bone. Physiotherapy plays a key role in restoring strength and mobility post-surgery. Early mobilization is crucial to prevent stiffness and muscle atrophy, focusing on non-weight bearing exercises initially.
Tibial Plateau Fractures
Tibial plateau fractures occur at the top of the tibia, near the knee joint. These fractures can disrupt the knee’s stability and are often caused by high-energy trauma or falls. Treatment may involve surgery to realign and stabilize the bone with plates or screws. Physiotherapy focuses on restoring knee function, with early mobilization to prevent stiffness and promote weight-bearing progression. Gentle exercises, like range of motion and strengthening, are essential for recovery.
Complex vs. Simple Fractures
Complex fractures involve multiple bone fragments or articular surface damage, often requiring surgical intervention. Simple fractures, like clean breaks, are less severe and may heal with immobilization. Physiotherapy differs accordingly, focusing on stability and mobility restoration for complex fractures, while simple fractures emphasize early movement to prevent stiffness and promote faster recovery.
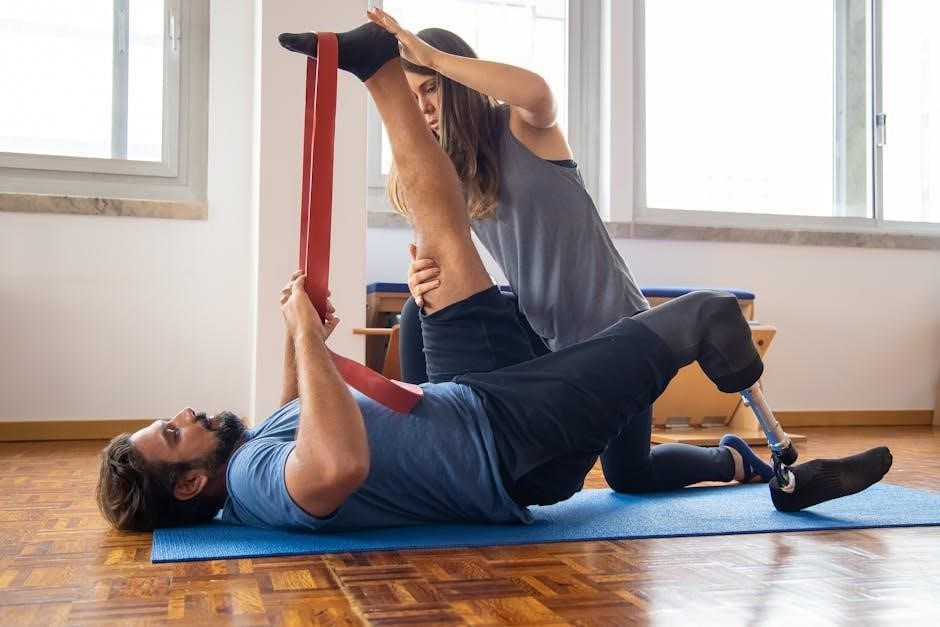

Immediate Post-Injury Management
Immediate post-injury management focuses on immobilization, pain relief, and swelling reduction. Proper wound care and stabilization are critical to prevent complications and prepare for physiotherapy.
Immobilization Techniques
Immobilization techniques, such as casts, braces, or splints, are essential to stabilize the tibia fracture, preventing further injury and promoting proper healing. External fixators may be used for complex fractures. These methods restrict movement, reducing pain and swelling, while allowing the bone to align and heal correctly. Proper immobilization is critical to ensure a strong foundation for subsequent rehabilitation exercises and physiotherapy interventions.
Pain Management Strategies
Pain management strategies for tibia fractures often include rest, ice therapy, and over-the-counter pain relievers to reduce discomfort and inflammation. Gentle exercises, even while immobilized, can help maintain joint mobility and reduce stiffness without putting stress on the fracture. A personalized approach, guided by a healthcare professional, ensures safe and effective recovery, preventing complications and promoting optimal healing.
Preparation for Physiotherapy
Preparation for physiotherapy after a tibia fracture involves medical clearance, setting realistic goals, and understanding the recovery process. Patients should gather necessary equipment like crutches or braces and wear comfortable clothing. Education on proper exercise techniques and safety precautions ensures adherence to the program. A tailored plan, created with a physiotherapist, addresses individual needs, promoting a smooth transition into rehabilitation.
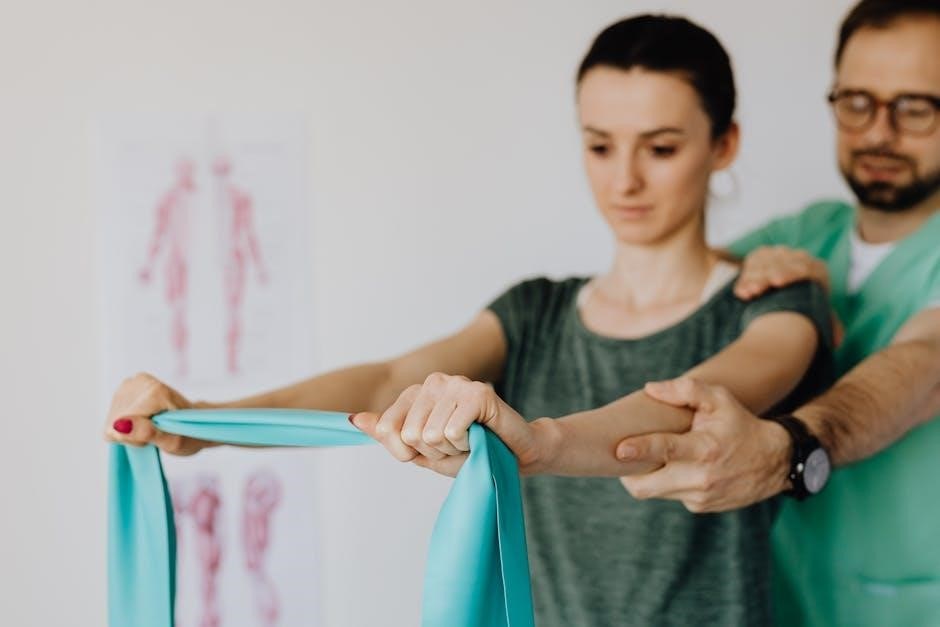

Phase 1: Early Stage Rehabilitation (0-6 weeks)
Non-Weight Bearing Exercises
Non-weight bearing exercises are essential during the early stages of tibia fracture recovery to avoid stressing the fracture site. These exercises include straight leg raises, ankle pumps, and heel slides, which help maintain muscle strength and joint mobility without putting pressure on the fractured bone. They are typically performed while seated or lying down to ensure compliance with weight-bearing restrictions. Patient education on proper technique is crucial to maximize benefits and prevent complications.
Range of Motion Exercises
Range of motion exercises are critical for maintaining joint mobility and preventing stiffness during tibia fracture recovery. These exercises, such as knee flexion, extension, and ankle rotations, are performed without weight-bearing to avoid stressing the fracture site. Gentle stretching and mobilization techniques are incorporated to improve flexibility and promote healing. Supervised by a physiotherapist, these exercises are gradually progressed to restore normal movement patterns and joint health.
Patient Education for Home Exercises
Patient education is vital for adherence to home exercise programs. Clear demonstrations and instructions ensure proper technique and safety. Emphasizing the importance of consistency and progression helps patients stay motivated. Providing printed or video resources reinforces learning. Education also addresses pain monitoring and when to seek help, ensuring a safe and effective recovery process at home.
Phase 2: Intermediate Stage Rehabilitation (6-12 weeks)
Focuses on progressive weight-bearing, strengthening exercises, and balance training to enhance lower limb function and prepare for advanced activities.
Progressive Weight Bearing
Progressive weight-bearing exercises are introduced to gradually increase load on the tibia, enhancing bone strength and promoting healing. Patients begin with non-weight-bearing activities, transitioning to partial weight-bearing with crutches or walkers. This phase focuses on improving tolerance to weight and restoring normal gait patterns. Specific exercises include partial weight-bearing stance and seated marching. Monitoring by a physiotherapist ensures proper alignment and progression.
Strengthening Exercises for the Lower Limb
Strengthening exercises target muscles around the tibia, such as quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves, to restore muscle balance and function. Exercises include straight leg raises, mini squats, and step-ups. Resistance bands or light weights may be incorporated to enhance muscle activation. These exercises improve joint stability and prepare the lower limb for weight-bearing activities, promoting a safer transition to mobility and daily tasks.
Balance and Proprioception Training
Balance and proprioception exercises are crucial for restoring stability and coordination after a tibia fracture. Techniques include single-leg stands, heel-to-toe walking, and wobble board exercises. These activities enhance neuromuscular control, reducing the risk of falls and improving overall mobility. Progression involves challenging surfaces or eyes-closed drills to advance proprioceptive awareness, ensuring safer and more confident movement patterns during recovery.
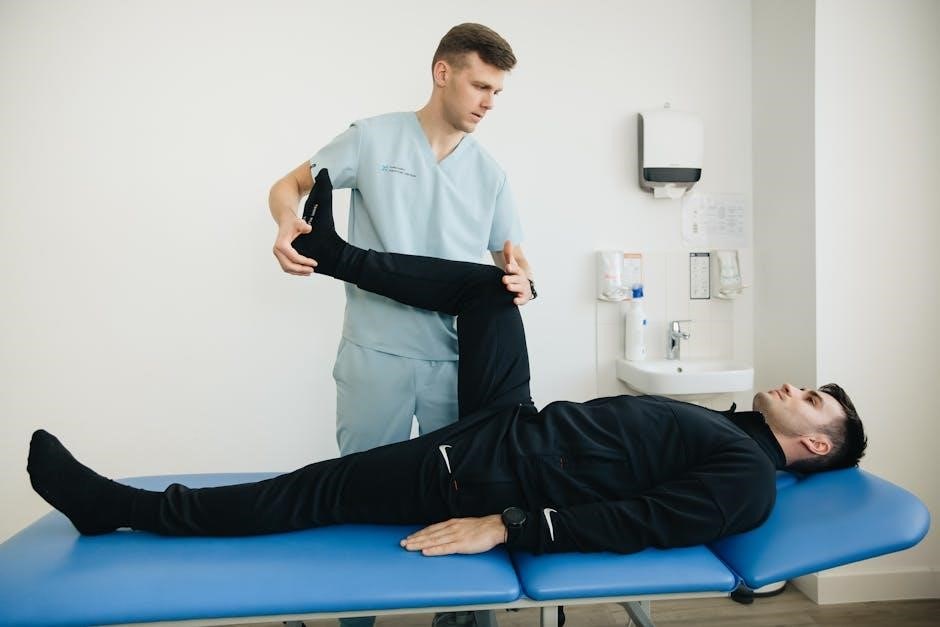
Phase 3: Advanced Stage Rehabilitation (3-6 months)
This phase focuses on functional strengthening, agility drills, and sport-specific activities to restore pre-injury mobility and prepare for return to daily activities or sports.
Functional Strengthening
Functional strengthening focuses on exercises that mimic daily activities and sports, like single-leg squats, step-ups, and balance training. These exercises enhance lower limb strength, stability, and coordination, preparing the patient for full-weight-bearing activities and reducing the risk of re-injury. Progression includes resistance bands, weights, and dynamic movements to restore muscle function and gait patterns, enabling a return to pre-injury independence and mobility.
Agility and Sport-Specific Drills
Agility drills, such as zigzag running and cone exercises, enhance speed, coordination, and quick directional changes. Sport-specific drills mimic the movements of the patient’s sport, like jumping or cutting, to restore functional abilities. These exercises improve neuromuscular control, preparing the patient for dynamic activities and ensuring a safe return to sports or physical pursuits, tailored to their progress and goals.
Return to Full Activity
Returning to full activity involves gradual progression to pre-injury levels, ensuring strength, flexibility, and joint stability are restored. Functional assessments and strength tests guide the transition. Clearance from healthcare providers is essential. Activities are tailored to individual needs, whether for daily living or sports, ensuring safe and confident resumption of prior functions without risking re-injury or complications.
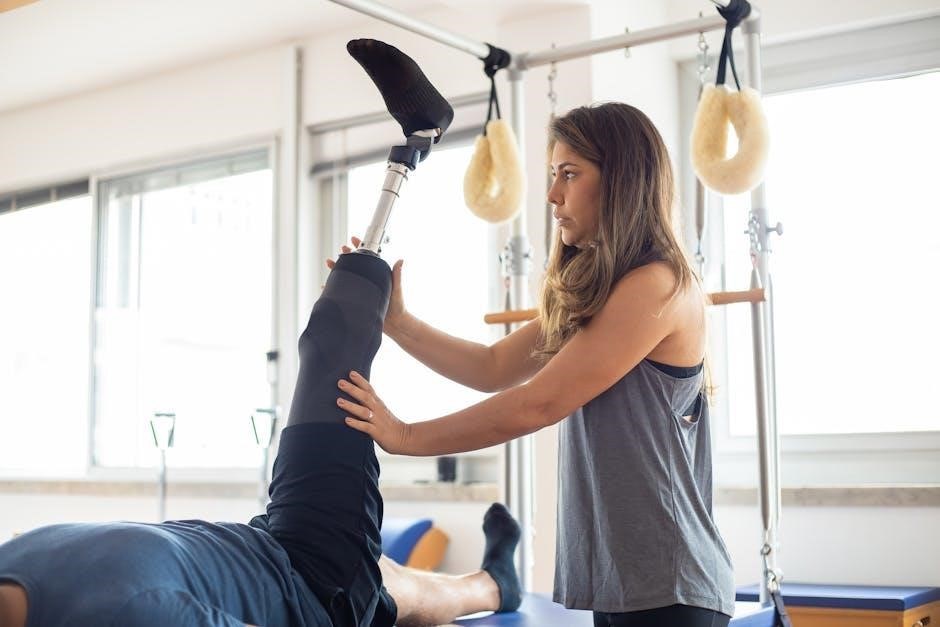

Key Physiotherapy Exercises for Tibia Fracture Recovery
Key exercises include heel slides, ankle pumps, straight leg raises, and step-ups, focusing on improving mobility, strength, and weight-bearing capacity to restore functional independence and movement.
Heel Slides and Ankle Pumps
Heel slides and ankle pumps are essential exercises for improving circulation and mobility post-tibia fracture. Heel slides involve slowly sliding the heel towards the buttocks while lying down, stretching the calf. Ankle pumps entail flexing and extending the foot to enhance range of motion. These exercises are typically performed while immobilized, promoting blood flow and preventing stiffness, aiding in early recovery without weight-bearing stress.
Straight Leg Raises
Straight leg raises are a foundational exercise in tibia fracture rehabilitation, targeting the quadriceps and hip flexors. Patients lift the affected leg straight while keeping the knee extended, strengthening muscles without putting stress on the fracture site. This exercise improves circulation, reduces muscle atrophy, and enhances stability around the knee and hip, aiding in early recovery and mobility restoration.
Step-Ups and Balance Training
Step-ups and balance training are advanced exercises for tibia fracture recovery, focusing on improving lower limb strength, coordination, and functional mobility. Patients perform step-ups on a low platform, gradually increasing height as strength improves. Balance exercises, such as single-leg stands, enhance proprioception and stability, reducing the risk of future injuries and promoting confident mobility during daily activities and sports.
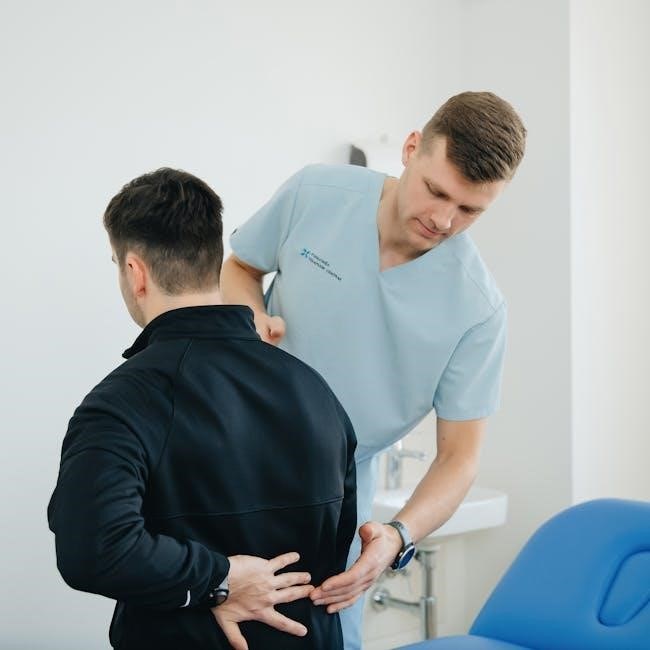
Rehabilitation Goals and Outcomes
Rehabilitation focuses on restoring mobility, strength, and function, aiming for a full recovery. Goals include achieving normal gait, improving balance, and ensuring functional independence for daily activities.
Restoring Knee Extension
Restoring knee extension is crucial for regaining normal gait and functional mobility. Physiotherapy focuses on exercises like straight leg raises and heel slides to strengthen quadriceps and improve joint mobility. These exercises help achieve full knee extension, essential for walking and daily activities. Gradual progression ensures proper healing and prevents complications, aiming to restore independence and normal movement patterns effectively.
Improving Gait Patterns
Improving gait patterns is essential for restoring normal walking ability after a tibia fracture. Physiotherapy focuses on exercises like gait training, step-ups, and balance drills to enhance strength and flexibility in the lower limb. These exercises help reduce compensatory movements and promote symmetrical walking. Gradual progression ensures proper alignment and efficiency, aiming to restore normal mobility and prevent long-term gait abnormalities.
Maximizing Functional Independence
Maximizing functional independence is a key goal in tibia fracture rehabilitation, enabling patients to regain control over daily activities. Exercises such as sit-to-stand, stair climbing, and single-leg stance improve strength, balance, and mobility. A physiotherapist tailors programs to address individual needs, ensuring safe progression. Consistency in these exercises is crucial for achieving independence and confidence in performing everyday tasks.
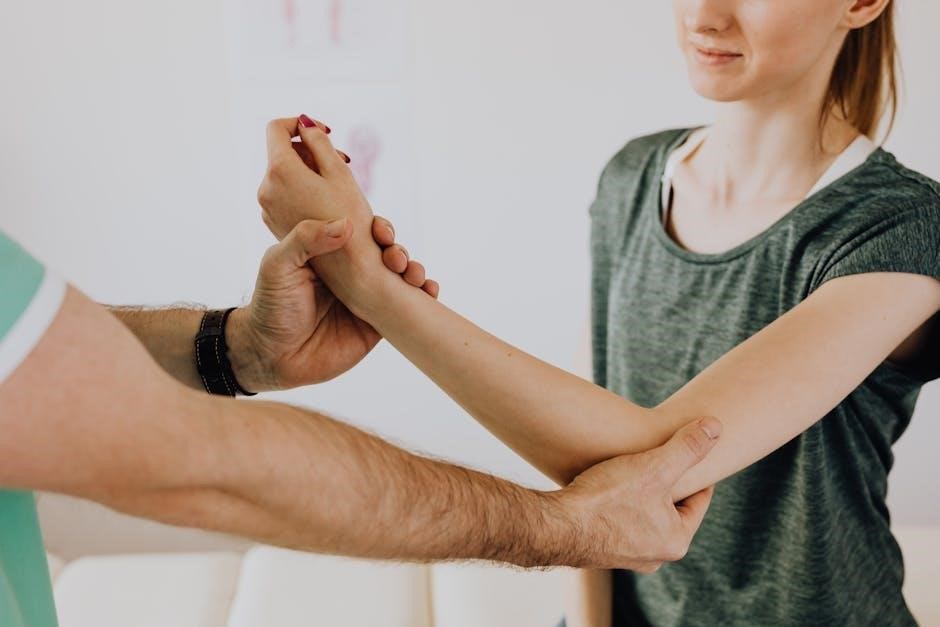

Common Challenges in Tibia Fracture Rehabilitation
Tibia fracture rehabilitation often involves managing pain, swelling, and limited mobility. Emotional challenges like frustration or anxiety can also arise, impacting recovery progress and adherence to therapy.
Managing Pain and Swelling
Pain and swelling are common challenges during tibia fracture rehabilitation. Techniques like cryotherapy, elevation, and compression help reduce swelling. Pain management may include analgesics or electrotherapy; Gentle exercises, such as ankle pumps, improve circulation without exacerbating discomfort. A physiotherapist can tailor strategies to individual needs, ensuring comfort and progress during recovery.
Overcoming Limited Mobility
Limited mobility after a tibia fracture can hinder daily activities and independence. Physiotherapy focuses on early mobilization through non-weight-bearing exercises, such as ankle pumps and heel slides, to promote healing and strengthen surrounding muscles. Gradually introducing weight-bearing activities and using assistive devices can restore normal movement. A tailored approach ensures patients regain functional independence and mobility safely and effectively.
Psychological Aspects of Recovery
Recovering from a tibia fracture can lead to emotional challenges, such as anxiety, depression, or frustration due to reduced mobility. Mental health support is crucial to address these issues. Setting realistic goals and celebrating small achievements can boost morale. Physiotherapists play a key role in providing encouragement and fostering a positive mindset, helping patients stay motivated throughout the recovery journey.
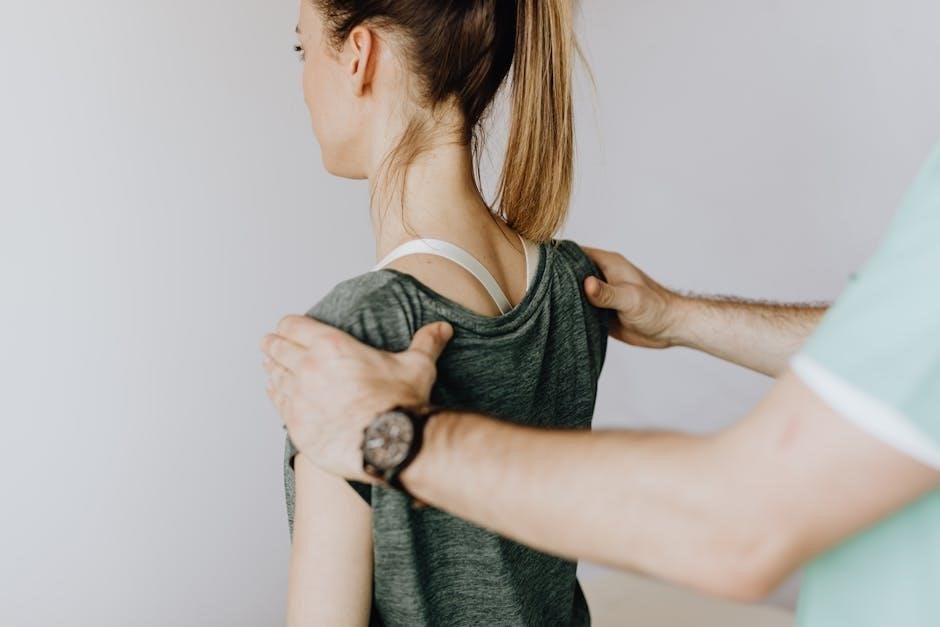

Physiotherapy Modalities and Tools
Physiotherapy utilizes tools like exercise bands, balance boards, and ultrasound therapy to aid recovery. These modalities enhance strength, flexibility, and balance, promoting effective healing and mobility restoration.
Use of Braces and Supports
The use of braces and supports in tibia fracture rehabilitation provides stability and alignment, reducing stress on the fracture site. Knee braces and orthotics are commonly used to immobilize or assist movement, promoting proper healing. These devices help manage pain and prevent deformities, allowing patients to gradually resume weight-bearing activities without compromising the fracture’s integrity or causing muscle atrophy during the recovery process.
Cryotherapy and Heat Therapy
Cryotherapy, such as icing, reduces inflammation and pain in the acute phase of tibia fracture recovery. Heat therapy, including warm compresses or baths, promotes blood flow and muscle relaxation. These modalities are often alternated to manage swelling and improve comfort. Cryotherapy is typically used in the initial stages, while heat therapy becomes more beneficial as healing progresses and mobility increases.
Electrotherapy for Pain Relief
Electrotherapy, such as TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) and EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation), is used to manage pain and promote healing. TENS blocks pain signals to the brain, while EMS strengthens muscles without movement. These modalities are applied via surface electrodes and are particularly useful in reducing discomfort during early rehabilitation phases, enhancing the effectiveness of physiotherapy exercises for tibia fractures.
Preventing Future Fractures
Focuses on strategies to enhance bone health, improve strength, and reduce fall risks through balanced diets, strengthening exercises, proper footwear, and safe living environments.
Bone Strengthening Exercises
Bone strengthening exercises are essential for improving bone density and reducing fracture risk. Weight-bearing activities like walking, jogging, and resistance training stimulate bone growth. Resistance bands, light weights, and bodyweight exercises can enhance lower limb stability. Regular physical activity, guided by a physiotherapist, helps rebuild bone strength and prevent future tibia fractures, ensuring long-term mobility and independence.
falls Prevention Strategies
Falls Prevention Strategies
Falls prevention strategies are crucial for individuals recovering from tibia fractures. Remove tripping hazards, ensure proper lighting, and use assistive devices like canes or walkers for stability. Non-slip footwear and handrails in bathrooms or staircases can reduce fall risks. Home modifications, such as raised toilet seats, improve safety. Regular balance training and medication reviews further minimize fall-related injuries.
Nutritional Advice for Bone Health
‘ under the topic ‘tibia fracture physiotherapy exercises pdf’. First, I should make sure I understand the scope and requirements of the task.
I should start by brainstorming the key points related to nutrition that support bone health after a tibia fracture. Important nutrients include calcium and vitamin D, as they are essential for bone healing and density. Protein is another critical component for tissue repair. I should mention foods rich in these nutrients, like dairy products, leafy greens, fortified foods, lean meats, and fish.
Additionally, staying hydrated is important for overall health, and limiting caffeine and alcohol can prevent interference with calcium absorption. I should also touch on the importance of a balanced diet tailored to individual needs, possibly under the guidance of a dietitian or healthcare provider.
Let me draft the content:
“Proper nutrition plays a vital role in tibia fracture recovery. Ensure adequate calcium intake through dairy products and leafy greens. Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, found in fortified foods and sunlight. Protein-rich foods like lean meats and fish support tissue repair. Stay hydrated and limit caffeine and alcohol, which can hinder calcium absorption. A balanced diet tailored to individual needs, guided by a dietitian, promotes optimal bone healing and overall recovery.”
Now, let’s count the words to make sure it’s exactly . Let’s see:
Proper
nutrition
plays
a
vital
role
in
tibia
fracture
recovery.
Ensure
adequate
calcium
intake
through
dairy
products
and
leafy
greens.
Vitamin
D
is
essential
for
calcium
absorption,
found
in
fortified
foods
and
sunlight.
Protein-rich
foods
like
lean
meats
and
fish
support
tissue
repair.
Stay
hydrated
and
limit
caffeine
and
alcohol,
which
can
hinder
calcium
absorption.
A
balanced
diet
tailored
to
individual
needs,
guided
by
a
dietitian,
promotes
optimal
bone
healing
and
overall
recovery.
Oops, that’s . I need to cut it down to 61. Let me revise:
“Proper nutrition is vital for tibia fracture recovery. Ensure adequate calcium through dairy and leafy greens. Vitamin D, found in fortified foods and sunlight, aids calcium absorption. Protein from lean meats and fish supports tissue repair. Stay hydrated and limit caffeine and alcohol to avoid hindering calcium absorption. A balanced diet tailored to individual needs, guided by a dietitian, promotes optimal bone healing and recovery.”
Counting again:
Proper
nutrition
is
vital
for
tibia
fracture
recovery.
Ensure
adequate
calcium
through
dairy
and
leafy
greens.
Vitamin
D,
found
in
fortified
foods
and
sunlight,
aids
calcium
absorption.
Protein
from
lean
meats
and
fish
supports
tissue
repair.
Stay
hydrated
and
limit
caffeine
and
alcohol
to
avoid
hindering
calcium
absorption.
A
balanced
diet
tailored
to
individual
needs,
guided
by
a
dietitian,
promotes
optimal
bone
healing
and
recovery.
Still over. Let me try to make it more concise:
“Proper nutrition is vital for tibia fracture recovery. Ensure adequate calcium through dairy and leafy greens. Vitamin D, found in fortified foods and sunlight, aids calcium absorption. Protein from lean meats and fish supports tissue repair. Limit caffeine and alcohol to avoid hindering calcium absorption. A balanced diet tailored to individual needs, guided by a dietitian, promotes optimal bone healing and recovery.”
Counting:
Proper
nutrition
is
vital
for
tibia
fracture
recovery.
Ensure
adequate
calcium
through
dairy
and
leafy
greens.
Vitamin
D,
found
in
fortified
foods
and
sunlight,
aids
calcium
absorption.
Protein
from
lean
meats
and
fish
supports
tissue
repair.
Limit
caffeine
and
alcohol
to
avoid
hindering
calcium
absorption.
A
balanced
diet
tailored
to
individual
needs,
guided
by
a
dietitian,
promotes
optimal
bone
healing
and
recovery.
Still . I need to remove one more word. Perhaps “and recovery” can be adjusted. Maybe:
“Proper nutrition is vital for tibia fracture recovery. Ensure adequate calcium through dairy and leafy greens. Vitamin D, found in fortified foods and sunlight, aids calcium absorption. Protein from lean meats and fish supports tissue repair. Limit caffeine and alcohol to avoid hindering calcium absorption. A balanced diet tailored to individual needs, guided by a dietitian, promotes optimal bone healing.”
Now, let’s count:
Proper
nutrition
is
vital
for
tibia
fracture
recovery.
Ensure
adequate
calcium
through
dairy
and
leafy
greens.
Vitamin
D,
found
in
fortified
foods
and
sunlight,
aids
calcium
absorption.
Protein
from
lean
meats
and
fish
supports
tissue
repair.
Limit
caffeine
and
alcohol
to
avoid
hindering
calcium
absorption.
A
balanced
diet
tailored
to
individual
needs,
guided
by
a
dietitian,
promotes
optimal
bone
healing
and
recovery.
Still . Maybe I can remove “and recovery” and end with “healing”:
“Proper nutrition is vital for tibia fracture recovery. Ensure adequate calcium through dairy and leafy greens. Vitamin D, found in fortified foods and sunlight, aids calcium absorption. Protein from lean meats and fish supports tissue repair. Limit caffeine and alcohol to avoid hindering calcium absorption. A balanced diet tailored to individual needs, guided by a dietitian, promotes optimal bone healing.”
Now, counting:
Proper
nutrition
is
vital
for
tibia
fracture
recovery.
Ensure
adequate
calcium
through
dairy
and
leafy
greens.
Vitamin
D,
found
in
fortified
foods
and
sunlight,
aids
calcium
absorption.
Protein
from
lean
meats
and
fish
34
Consistent adherence to physiotherapy exercises is crucial for optimal tibia fracture recovery. Regular practice ensures restored mobility, strength, and long-term bone health, enabling a full return to daily activities.
Importance of Consistency in Rehabilitation
Consistency in performing tibia fracture physiotherapy exercises ensures proper tissue repair and muscle strength recovery. Regular adherence prevents setbacks, promoting gradual improvement in mobility and function. It also helps maintain motivation and adherence to the rehabilitation plan, which are critical for achieving long-term recovery goals and restoring independence.
Long-Term Benefits of Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy after a tibia fracture enhances long-term mobility, strength, and flexibility, reducing the risk of chronic pain or stiffness. It promotes full functional recovery, enabling individuals to return to daily activities and sports confidently. Consistent therapy also improves joint stability and overall lower limb function, ensuring sustained independence and quality of life.
Encouraging Patient Adherence
Encouraging patient adherence to physiotherapy routines is crucial for optimal recovery. Setting clear, achievable goals and providing positive reinforcement fosters motivation. Regular feedback and involving patients in goal-setting empower them to take ownership of their rehabilitation. Using reminders, educational materials, and technology, such as mobile apps, can also enhance adherence and ensure consistent progress in tibia fracture recovery.
